Err Object
If you are not familiar with Error Handling yet, we highly recommend you to read this example first. When an error in Excel VBA occurs, the properties of the Err object are filled with information.
Situation:
The program below calculates the square root of numbers.
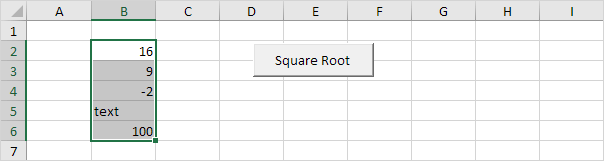
1. Place a command button on your worksheet and add the following code lines:
Dim rng As Range, cell As Range
Set rng = Selection
For Each cell In rng
On Error GoTo InvalidValue:
cell.Value = Sqr(cell.Value)
Next cell
Exit Sub
InvalidValue:
MsgBox Err.Number & ” ” & Err.Description & ” at cell ” & cell.Address
Resume Next
Result when you select Range(“B2:B6”) and click the command button on the sheet:
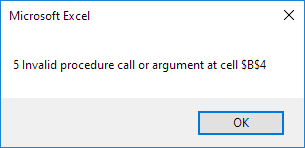
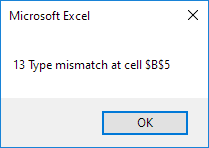
Explanation: when an error occurs, the number property of the Err object is filled with an unique error number of the current error and the Description property is filled with the error description of the current error.
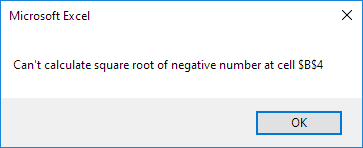
2. These descriptions may not be very helpful to the users of your program. You can make the error messages more user friendly by modifying the last part of the macro as follows:
InvalidValue:
Select Case Err.Number
Case Is = 5
MsgBox “Can’t calculate square root of negative number at cell ” & cell.Address
Case Is = 13
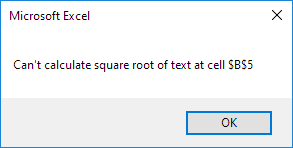
MsgBox “Can’t calculate square root of text at cell ” & cell.Address
End Select
Resume Next
Tip: go through our Select Case program to learn more about the Select Case structure.
Result:
Next Chapter: String Manipulation




