Arithmetic Operators
The arithmetic operators are used in a PowerShell to perform the calculation of the numeric values. By using the arithmetic operators, we can add (+), subtract (-), multiply (*), or divide (/) the values. These operators also include the modulus (%) operator to calculate the remainder of the division operation.
In PowerShell, the addition and multiplication operator may also be used with the strings, hash tables, and arrays. The multiplication (*) operator returns more than one copy of the input, and addition (+) operator concatenates the input.
Windows PowerShell supports the following arithmetic operators:
- + (Addition)
- – (Subtraction)
- * (Multiplication)
- / (Division)
- % (Modulus)
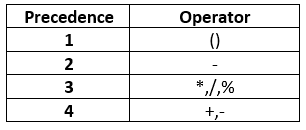
Arithmetic Operators Precedence
PowerShell processes these type of operators in expression according to the following precedence rules:
Addition Operator (+)
The addition operator is an arithmetic operator, which is used to add the two numbers, strings, arrays, and hash tables.
Examples:
Example1: This example adds two numeric values:
The last command will display the value of the variable $c as 30.
Example2: This example adds two strings:
The last command will display the value of the variable $z as a single string “PowerShell“.
Example3: This example adds two arrays:
The last command will display the following result of an array $z:
1 2 3 A B C
Subtraction Operator (-)
The subtraction operator is an arithmetic operator, which is used to subtract one numeric value from another numeric value and make a number to a negative number.
Examples:
Example1: This example subtract one numeric value from other value:
The last command will display the value of the variable $c as 10.
Example2: This example makes a number to a negative number:
The last command will display the value of the variable $c as -10.
Multiplication Operator (*)
The Multiplication operator is an arithmetic operator, which is used to multiply the numeric values or copy the string and array values to the specified number of times.
Examples:
Example1: This example multiplies two numeric values:
The last command will display the value of the variable $c as 200.
Example2: This example is used to create the copies of the string according to a number which is specified after the multiplication operator:
The last command will display the value of the variable $y as a single string “ShellShell“.
Example3: This example is used to create the copies of array values according to a number which is specified after the multiplication operator:
The last command will display the following result of an array $y:
1 2 3 1 2 3
Division Operator (/)
The Division operator is an arithmetic operator which is used to divide the two numeric values.
The following example divides the two numeric values:
The last command will display the value of the variable $c as 2.5.
Modulus Operator (%)
The modulus operator is an arithmetic operator which is used to calculate the remainder of the division operation
The following example calculates the modulus of the two numeric values:
The last command will display the value of the variable $c as 2.




