Formula Errors
##### error | #NAME? error | #VALUE! error | #DIV/0! error | #REF! error
This chapter teaches you how to deal with some common formula errors in Excel.
##### error
When your cell contains this error code, the column isn’t wide enough to display the value.
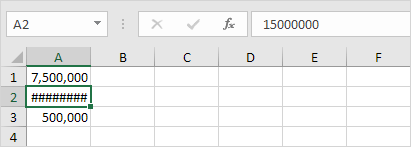
1. Click on the right border of the column A header and increase the column width.
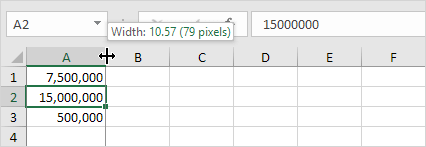
Tip: double click the right border of the column A header to automatically fit the widest entry in column A.
#NAME? error
The #NAME? error occurs when Excel does not recognize text in a formula.
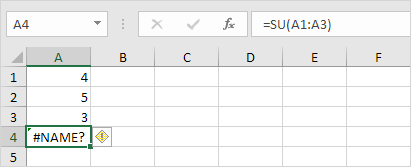
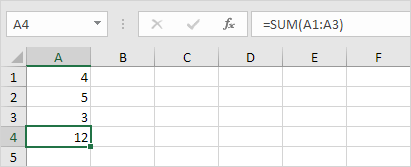
1. Simply correct SU to SUM.
#VALUE! error
Excel displays the #VALUE! error when a formula has the wrong type of argument.
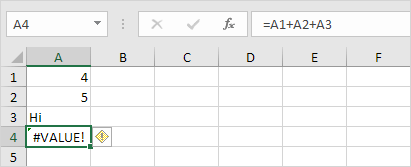
1a. Change the value of cell A3 to a number.
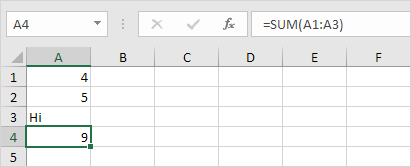
1b. Use a function to ignore cells that contain text.
#DIV/0! error
Excel displays the #DIV/0! error when a formula tries to divide a number by 0 or an empty cell.
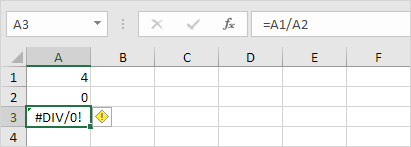
1a. Change the value of cell A2 to a value that is not equal to 0.
1b. Prevent the error from being displayed by using the logical function IF.
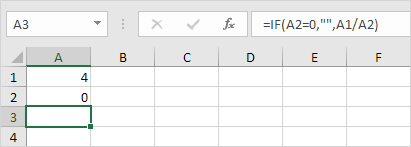
Explanation: if cell A2 equals 0, an empty string (“”) is displayed. If not, the result of the formula A1/A2 is displayed.
#REF! error
Excel displays the #REF! error when a formula refers to a cell that is not valid.
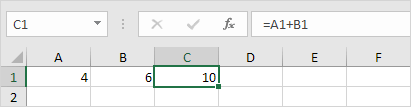
1. Cell C1 references cell A1 and cell B1.
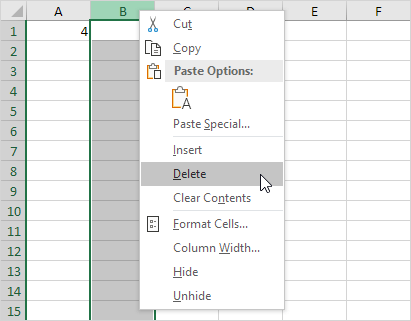
2. Delete column B. To achieve this, right click the column B header and click Delete.
3. Select cell B1. The reference to cell B1 is not valid anymore.
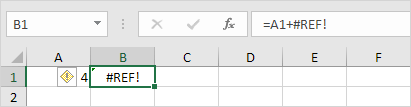
4. To fix this error, you can either delete +#REF! in the formula of cell B1 or you can undo your action by pressing CTRL + z
Next Chapter: Array Formulas




