How To Test Statistical Significance By T-Test
Array1 (Required): Range for dataset 1
Array2 (Required): Range for dataset 2
Tails (Required): This determines if it is a one-tail T-test or two tail T-test.
- One tail T-test
- Two tail T test
Type (required): Type of t-test
- Paired T-test, i.e. if the two data sets are related to each other
- Unpaired T-test, the two samples have equal variance
- Unpaired T-test , the two samples have unequal variance
Example:
1. Consider the following dataset for T-test.
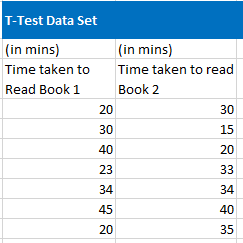
2. Select the two –datasets in array 1 and array 2.
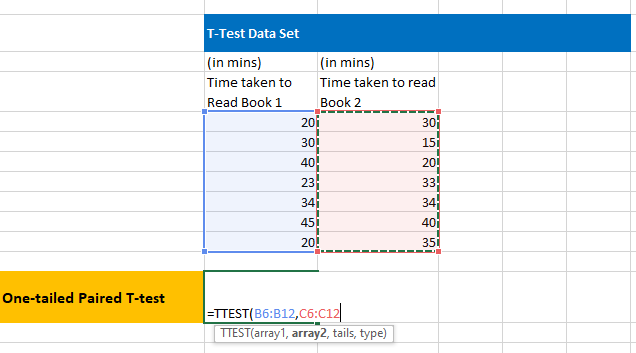
3. On an Empty Cell, write the formula to perform 1-tail Paired T test
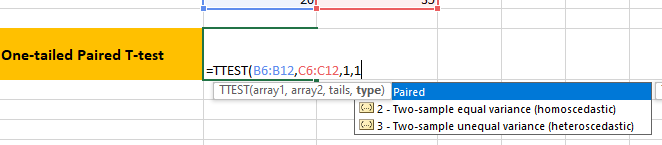
Probability obtained

4. Similarly, perform a two–tailed paired T test
![]()
Probability Obtained
![]()
Based on the obtained value you can accept or reject the null hypothesis. If the T-test gives the probability less than 0.05, then reject the null hypothesis. This means there is less than 5% probability that the null hypothesis is true.
Here, in both cases, p-value> 0.05. So, we accept the null hypothesis.
- #NUM! – If the arguments for tail or type are not correct. Tail argument must be 1 or 2. Type argument must be 1,2 or 3.
- #N/A! – The datasets are of different length
- #VALUE – The tail-argument or the type argument are non-numeric
Template
Further reading: Basic concepts Getting started with Excel Cell References




